Center for Innovative and Strategic Transformation of Alkane Resources
CISTAR Vision
To create a transformative engineered system to convert light hydrocarbons from shale resources to chemicals and transportation fuels in smaller, modular, local, and highly networked processing plants.
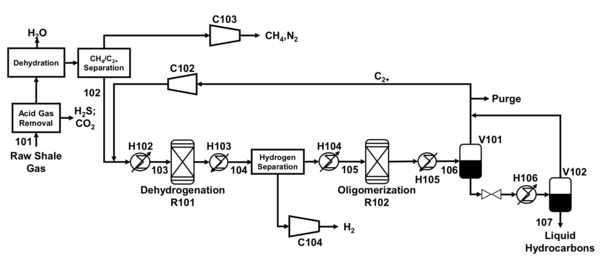
Baseline CISTAR Process. Source: T. Ridha et al., “Valorization of Shale Gas Condensate to Liquid Hydrocarbons through Catalytic Dehydrogenation and Oligomerization”, Processes, vol. 6, no. 9, p. 139, 2018.
Oligomerization Reactor Modeling and Optimization
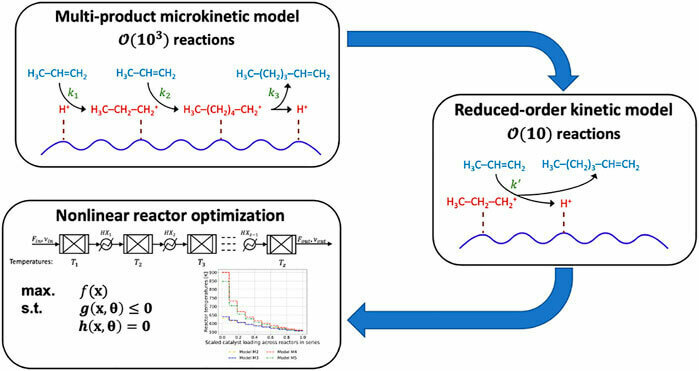
Despite the success of multiscale modeling in science and engineering, embedding molecular-level information into nonlinear reactor design and control optimization problems remains challenging. In this work, we propose a computationally tractable scale-bridging approach that incorporates information from multi-product microkinetic (MK) models with thousands of rates and chemical species into nonlinear reactor design optimization problems. We demonstrate reduced-order kinetic (ROK) modeling approaches for catalytic oligomerization in shale gas processing. We assemble a library of six candidate ROK models based on literature and MK model structure. We find that three metrics—quality of fit (e.g., mean squared logarithmic error), thermodynamic consistency (e.g., low conversion of exothermic reactions at high temperatures), and model identifiability—are all necessary to train and select ROK models. The ROK models that closely mimic the structure of the MK model offer the best compromise to emulate the product distribution. Using the four best ROK models, we optimize the temperature profiles in staged reactors to maximize conversions to heavier oligomerization products. The optimal temperature starts at 630–900K and monotonically decreases to approximately 560 K in the final stage, depending on the choice of ROK model. For all models, staging increases heavier olefin production by 2.5% and there is minimal benefit to more than four stages. The choice of ROK model, i.e., model-form uncertainty, results in a 22% difference in the objective function, which is twice the impact of parametric uncertainty; we demonstrate sequential eigendecomposition of the Fisher information matrix to identify and fix sloppy model parameters, which allows for more reliable estimation of the covariance of the identifiable calibrated model parameters. First-order uncertainty propagation determines this parametric uncertainty induces less than a 10% variability in the reactor optimization objective function. This result highlights the importance of quantifying model-form uncertainty, in addition to parametric uncertainty, in multi-scale reactor and process design and optimization. Moreover, the fast dynamic optimization solution times suggest the ROK strategy is suitable for incorporating molecular information in sequential modular or equation-oriented process simulation and optimization frameworks.
Related Publications
Kanishka Ghosh*, Sergio Vernuccio, Alexander W. Dowling (2022). Nonlinear Reactor Design Optimization With Embedded Microkinetic Model Information. Frontiers in Chemical Engineering, 4, 898685. [link]
Kanishka Ghosh* and Alexander W. Dowling. Beyond R2: Cautionary Tales Using Reduced-Order Kinetic Models for Reactor Optimization, AIChE Annual Meeting, Boston, MA, November 10, 2021. [link]
Kanishka Ghosh* and Alexander W. Dowling. Reduced-Order Kinetic Models and Reactor Optimization for Modular Shale Gas Utilization. AIChE Annual Meeting, November 18, 2020. [link]
Kanishka Ghosh* and Alexander W. Dowling. Reduced-order Kinetic Models and Reactor Optimization for Oligomerization in CISTAR. AIChE MRC, Chicago, IL, March 11, 2020. Oral Presentation. [link]
Kanishka Ghosh* and Alexander W. Dowling. Microkinetic Model Reduction for Ethylene Oligomerization Reactor Optimization and Design. AIChE Annual Meeting, Orlando, FL, November 12, 2019. Poster. [link]
Kanishka Ghosh* and Alexander W. Dowling. Microkinetic Model Reduction in Reactor Optimization for Oligomerization Reaction using CISTAR Technology. FOCAPD, Copper Mountain Resort, CO, July 14, 2019. Poster.
Support from NSF award Engineering Research Center for Innovative and Strategic Transformation of Alkane Resources – CISTAR EEC-1647722 and University of Notre Dame Office of Research.


Collaborators
Prof. Rakesh Agarwal, Purdue University
Prof. David Allen, University of Texas at Austin
Prof. Mark Stadtherr, University of Texas at Austin


